
VHF/UHF WSPR Propagation Study
and achieves an effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP) greater than 48 dBW and G/T greater than 7 dB/K. The port antenna has a hybrid function: it can support the lunar link or the DTE link, depending on line of sight conditions and mission demands. To support the lunar link function, it has a slightly larger antenna, with
PPT Satellite Communications A Part 3 PowerPoint Presentation, free
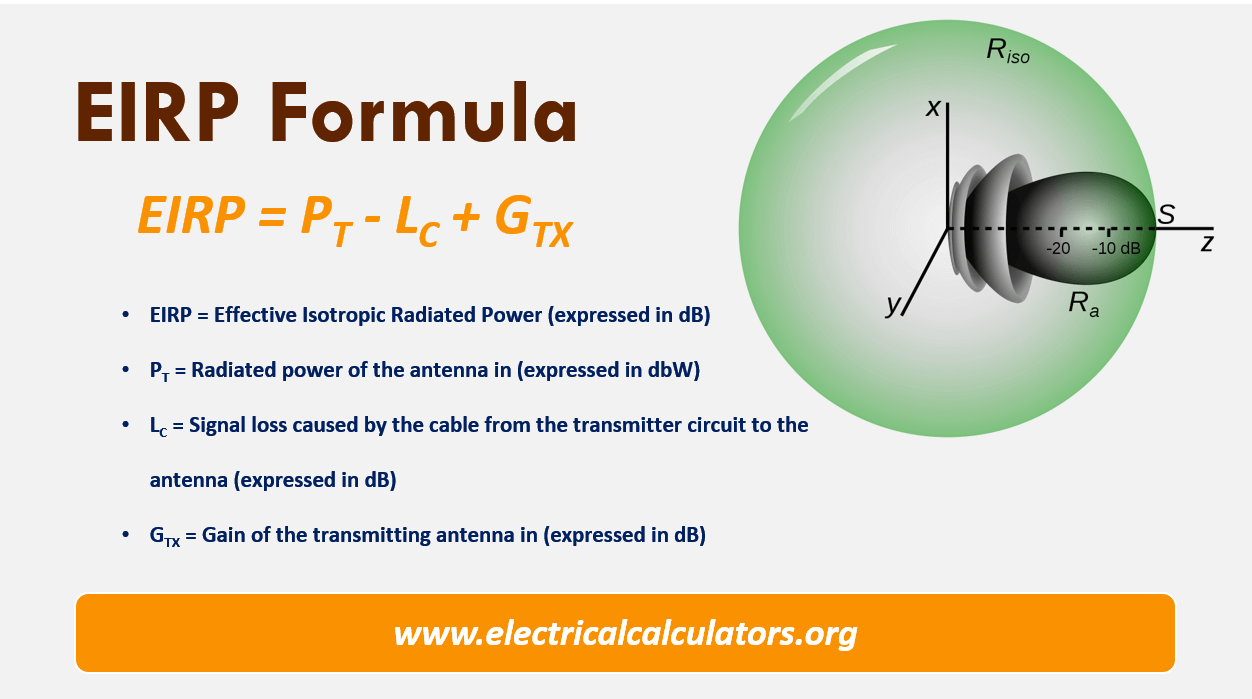
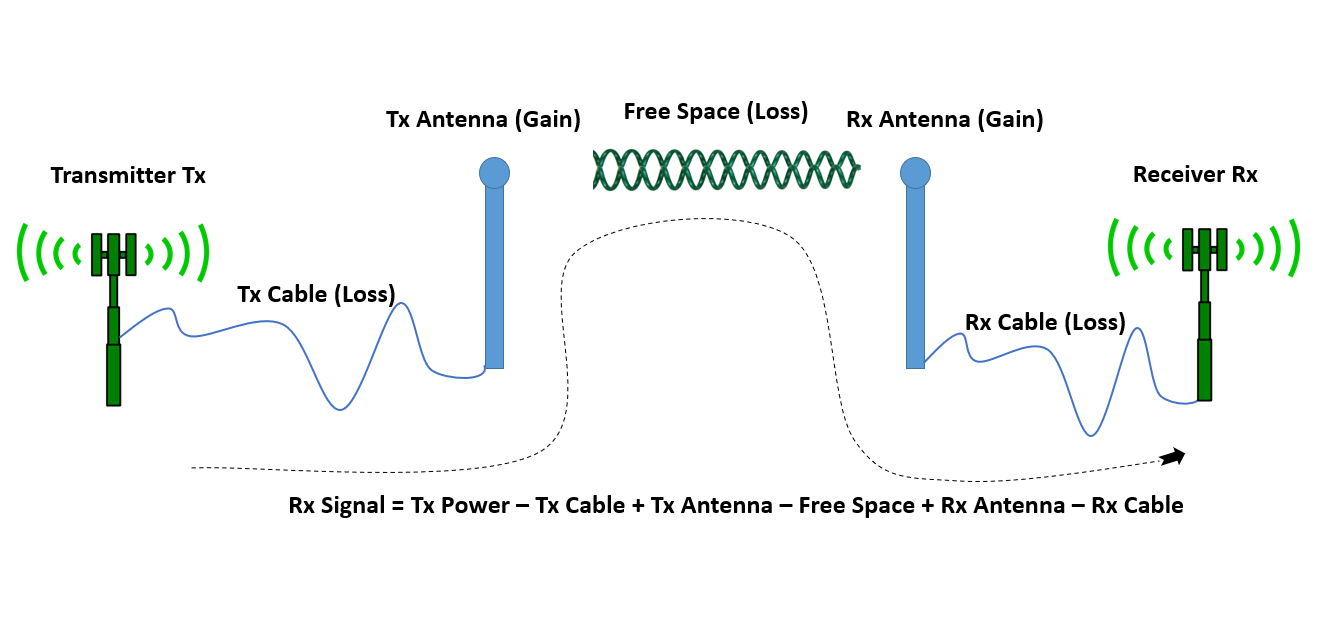
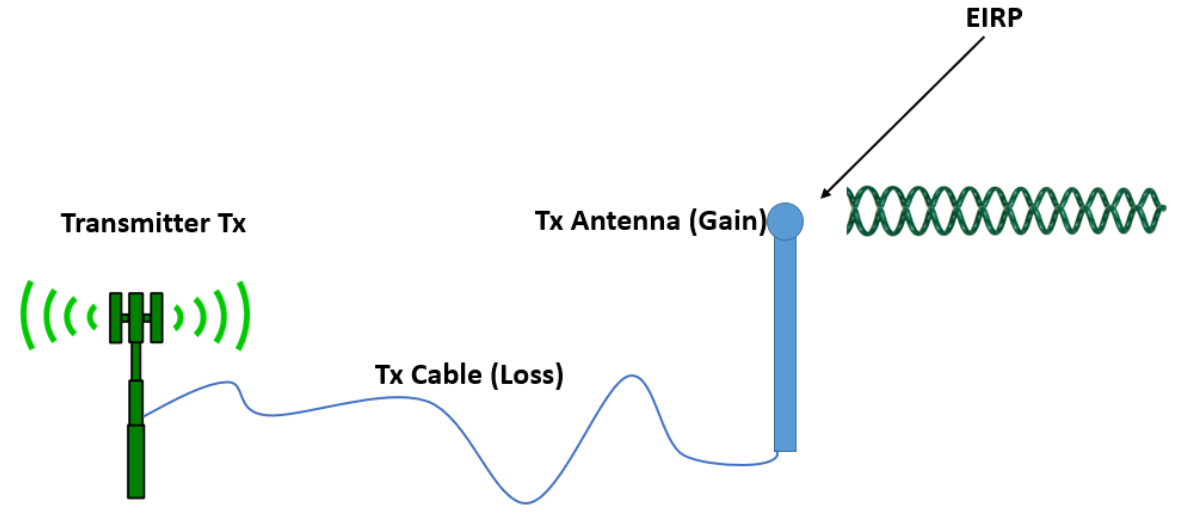
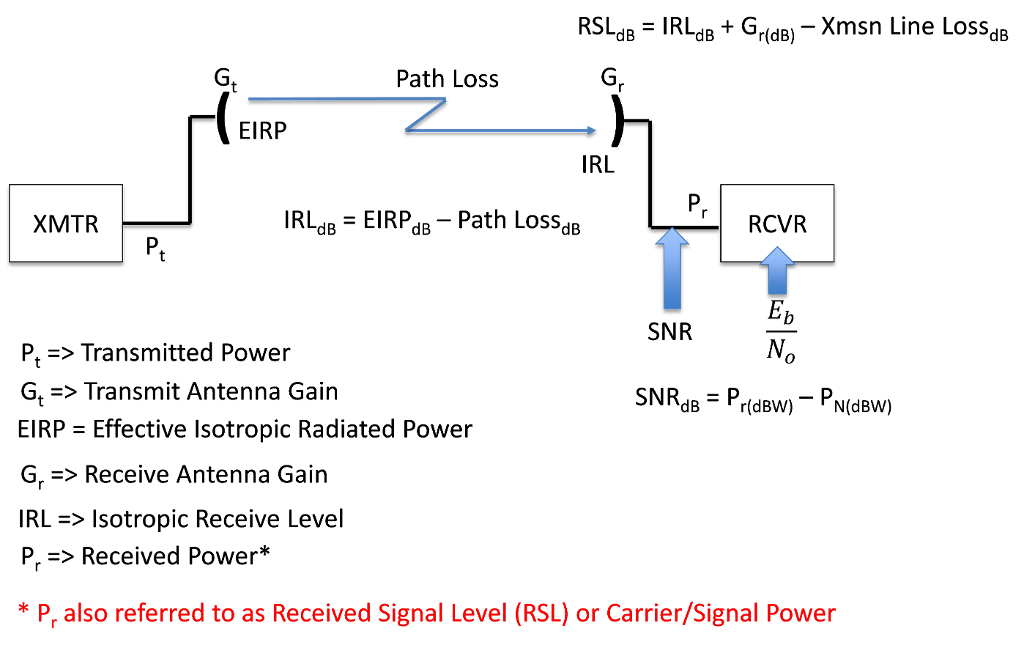
Effective Isotropic Radiated Power or Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) is the measured power radiated in a single direction by an ideal isotropic antenna. It is the antenna's maximum power output in the direction with the highest antenna gain. EIRP must take into account the connector-related power loss as well as transmission line.

11+ Effective Isotropic Radiated Power Calculation Pictures Leonard R
EIRP (Effective Isotropic Radiated Power) is the measured radiated power of an antenna in a specific direction. It is also called Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power. It is the output power when a signal is concentrated into a smaller area by the Antenna. The EIRP can take into account the losses in transmission line, connectors and includes.

Antenna Gain dBi vs. dBd Ham Radio Academy
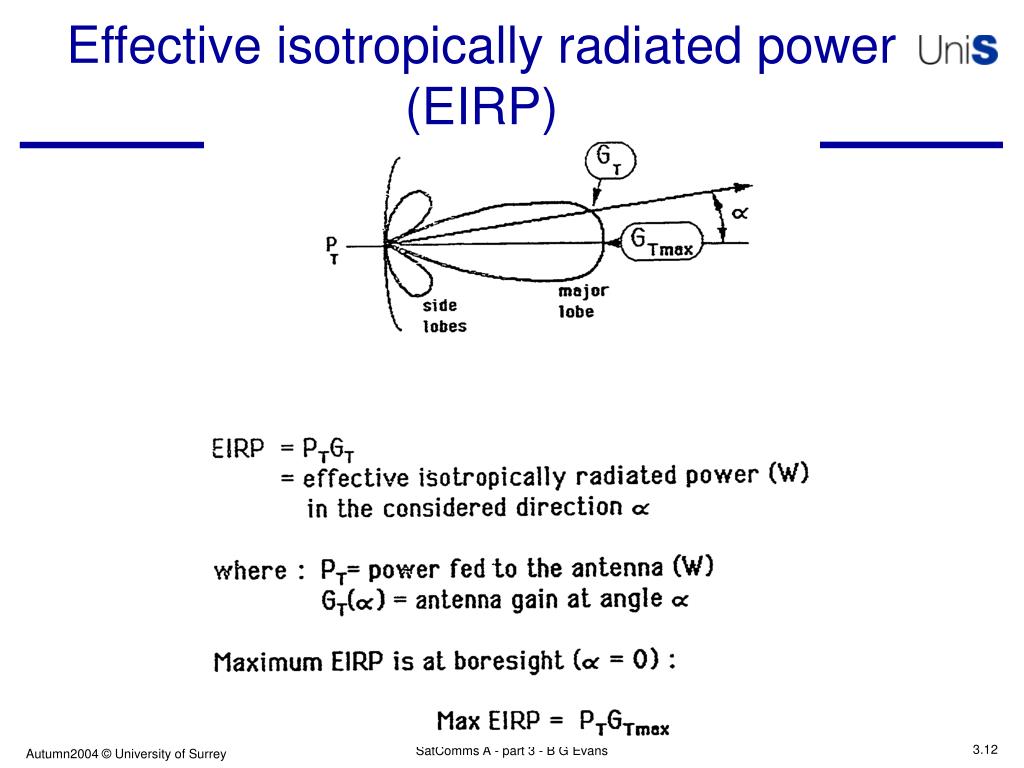
4.5.3 Effective Isotropic Radiated Power. A transmit antenna does not radiate power equally in all directions and for a receiver in the main lobe of the transmit antenna it is as though there is an isotropic transmit antenna with a much higher input power. This concept is incorporated in the effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP):
Iuwne10 S01 L03
Effective isotropic radiated power is the hypothetical power that would have to be radiated by an isotropic antenna to give the same ("equivalent") signal strength as the actual source antenna in the direction of the antenna's strongest beam. The difference between EIRP and ERP is that ERP compares the actual antenna to a half-wave dipole.
Effective Isotropic Radiated Power Formula Calculator Antenna EIRP
An antenna's effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP) is its power measured in one direction. It is named as such because it is the power an isotropic (perfectly omnidirectional) antenna would have to radiate to achieve the same value. This calculator is designed to compute the EIRP given the transmitter's radiated power, the loss introduced.
Презентация на тему "© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved
EIRP (Effective Isotropic Radiated Power) is a calculation used to estimate the radiated output power of an isotropic antenna (a theoretical half wave dipole antenna that radiates perfectly in all directions). This formula takes into account transmitter output power, cable loss, and antenna gain.
What is Effective Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP)? Study CCNP
Jan 5, 2018. Effective, or Equivalent, Isotropically Radiated Power (EIRP) is the maximum amount of power that could be radiated from an antenna, given its antenna gain and the transmitter power of the RF system. EIRP is most commonly given in decibels over isotropic, dBi. The IEEE definition for effective radiated power (ERP), which is similar.
What is Effective Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP)? Study CCNP
What is the effective isotropic radiated power of a repeater station with 200 W transmitter power output, 2 dB feed line loss, 2.8 dB duplexer loss, 1.2 dB circulator loss and 7 dBi antenna gain? System gain = -2 - 2.8 - 1.2 + 7 = 1 dB ERP 200 W log 100 log (0.1) 200 1.26 252 W11

Effective isotropic radiated power of the 16 × 16 (left) and 32 × 32
This document provides the guidelines for determining the effective radiated power (ERP) and equivalent isotropically radiated power (EIRP) of a radio frequency (RF) transmitting system. It explains the concepts and formulas of ERP and EIRP, and gives examples of how to apply them in different scenarios. It also includes a glossary of terms and references for further information.
PPT NETW 701Wireless Communications PowerPoint Presentation, free
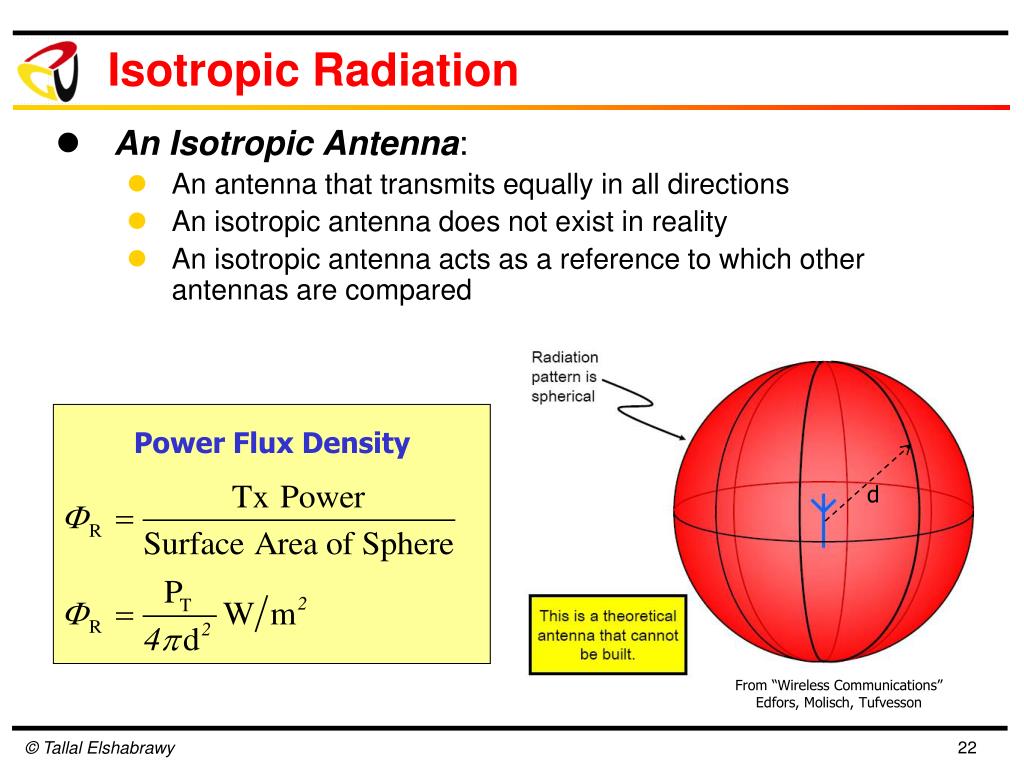
Effective isotropic radiated power (sometimes also referred to as equivalent isotropic radiated power), is a commonly used unit when specifying antenna efficiency (gain). In order to provide a common reference for radiated power, an ideal isotropic radiator is used as the standard. An isotropic radiator emits power from a singular point.

PPT bab Antenna PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID610001
Effective, or equivalent, isotropically radiated power (EIRP) is a measurement of the optimum power that can be radiated from an antenna from a particular transmitter. Most often conveyed as either decibels (dB), or decibels over isotropic (dBi), EIRP is used to gauge the maximum possible radiation from an RF system, either for standards.
Use The Following Information For Questions 1 To 1...
EIRP is Effective Isotropic Radiated Power, also called the Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power.In antenna measurements, the measured radiated power in a single direction (that is, for a fixed and ) is known as the EIRP. Typically, for an antenna radiation pattern measurement, if a single value of EIRP is given, this will be the maximum value of the EIRP over all measured angles.
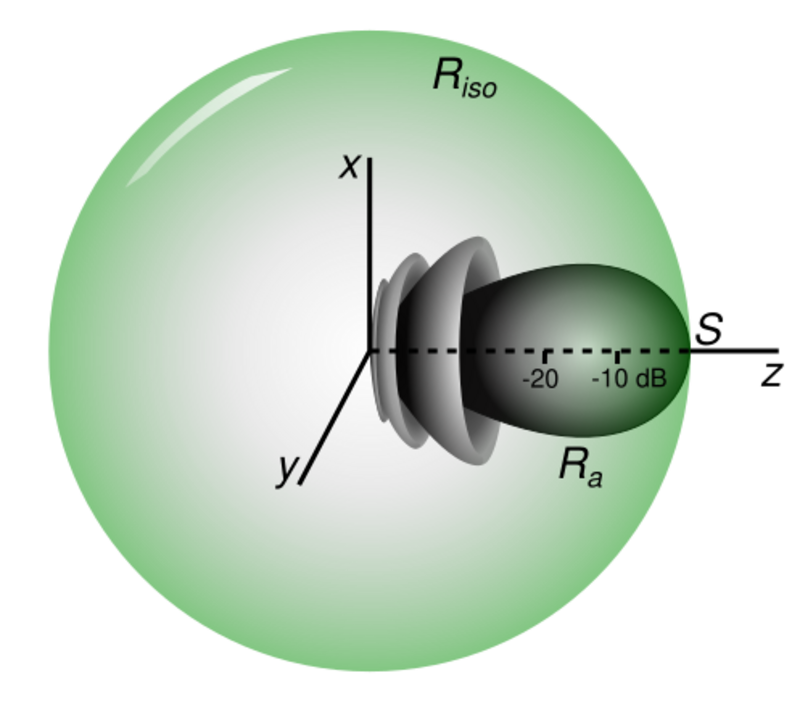
Effective radiated power HandWiki
Effective Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) is the output power when a signal is concentrated into a smaller area by the Antenna. An isotropic radiator radiates power equally in all directions, however a perfect isotropic radiator is only theoretical as even the simplest antennas will concentrate the signal in certain direction(s). E.g. a 1/2.
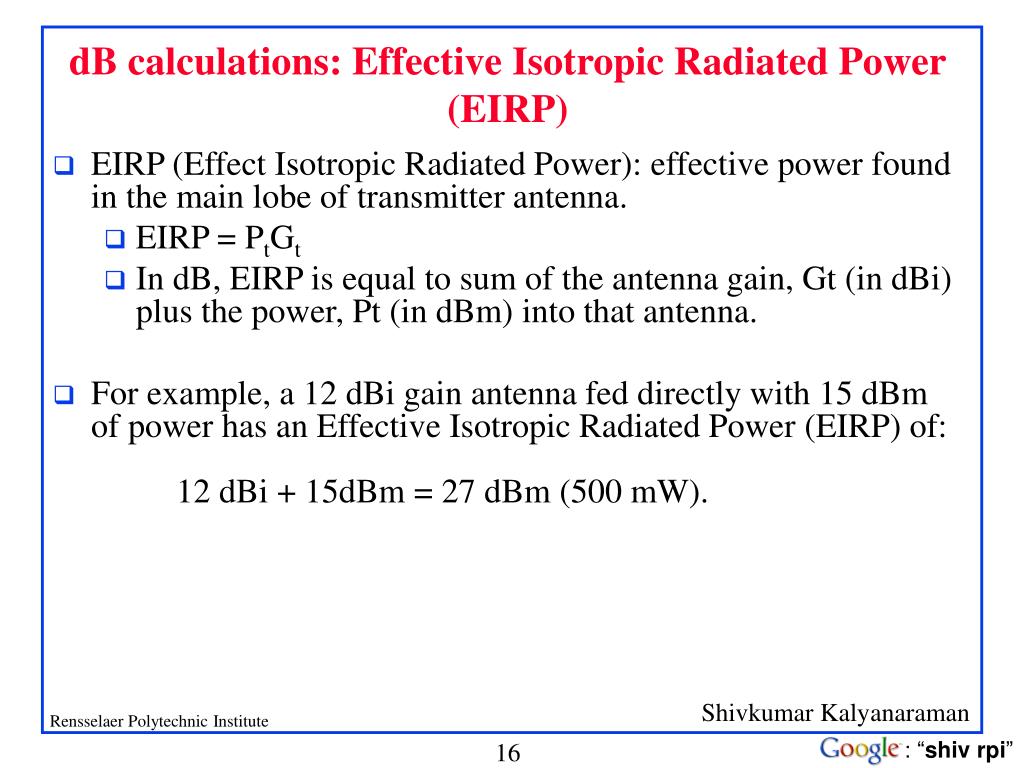
PPT ECSE 6961 The Wireless Channel PowerPoint Presentation, free
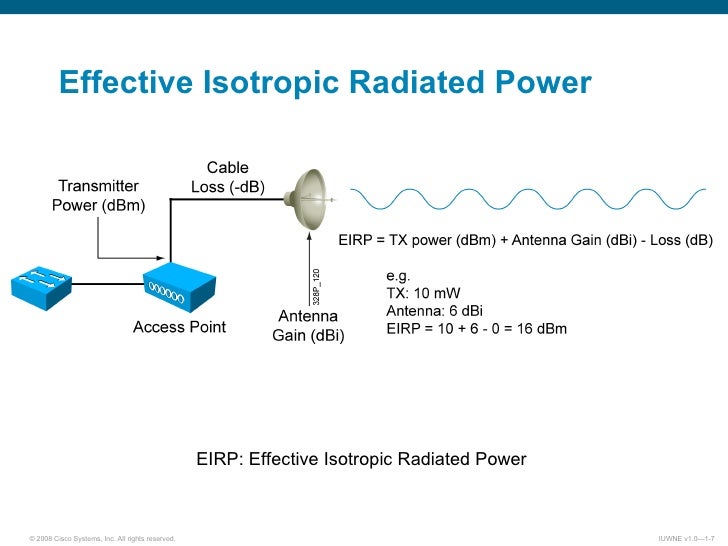
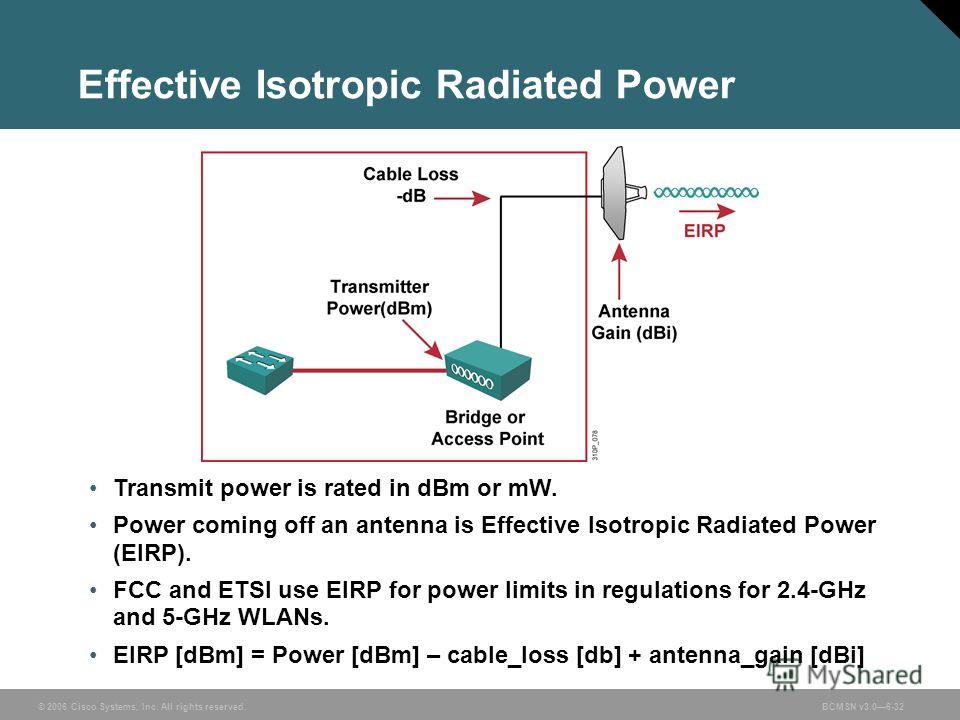
EIRP (Effective Isotropic Radiated Power) is the actual amount of signal leaving the antenna and is a value measured in db and is based on 3 values: a) Transmit Power (dBm) b) Cable Loss (dB) c) Antenna Gain (dBi) The dB measures the power of a signal as a function of its ratio to another standardized value. The abbreviation dB is often.

(PDF) Dynamic Calibration of GPS Effective Isotropic Radiated Power for
P d = P t / (4 π R 2) Pt is the total power radiated by the antenna. This formula works for the power being emitted by an isotropic antenna. If the antenna is a directional antenna, we need to take into account the antenna gain, and the formula used to calculate the power density is as follows: P d = ERP/ (4 π R 2) = (P t × A g )/ (4 π R 2)